Fire protection
with system
Buildings
- over 18 metres high (> 5 storeys) and/or
- small distances (1 metre) and/or
- problematic evacuation options often require increased fire protection.
Fire protection
Fire protection is active consumer protection and an existential necessity in high-density living spaces and high-rise buildings. Fire protection includes fire prevention, fire containment and firefighting.
Fire prevention
It includes all preventive measures that counteract the development of harmful fires. In particular, the fire resistance classes of building components and the building material classes of materials are regulated by law.
Fire limitation
Firefighting
In particular, the time between the outbreak of fire and effective countermeasures counts here. Facades or roofs made of membrane and foil constructions are no obstacle for the fire brigade.

TEROSON fire protection products
‘Fire prevention’ is the decisive area in chemical sealing.
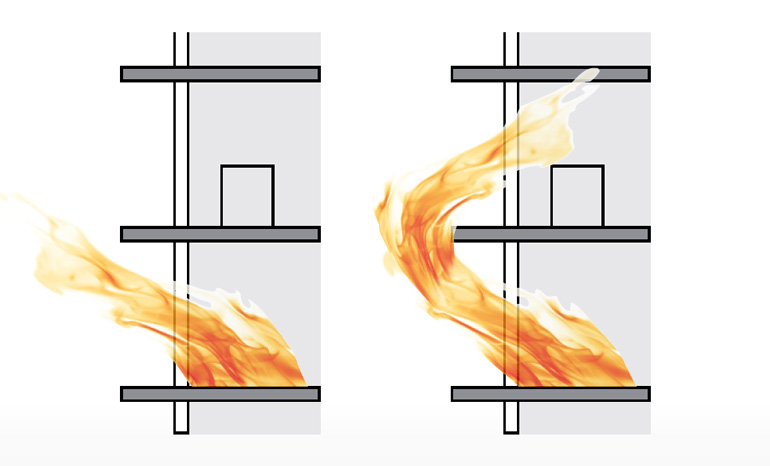
Assumed and actual shape of the flames
Regulations
DIN 4102 used to regulate/classify the fire behaviour of building materials in Germany. Building materials to be used in building construction must achieve at least the building material class ‘normally flammable’ and therefore ‘B2’. DIN 4102 has been expanded (as in other EU countries) to include EN 13501 with the categorisation of building materials into seven Euroclasses and the corresponding fire behaviour. Here, too, the building materials to be used must be at least ‘normally flammable’ and thus correspond to class ‘E’.
The classification of building materials according to DIN EN 13501 is as follows:
- Fire classification (A1-F) (fire resistance)
- Smoke development (s1-s3)
- Droplet formation (d0-d2)
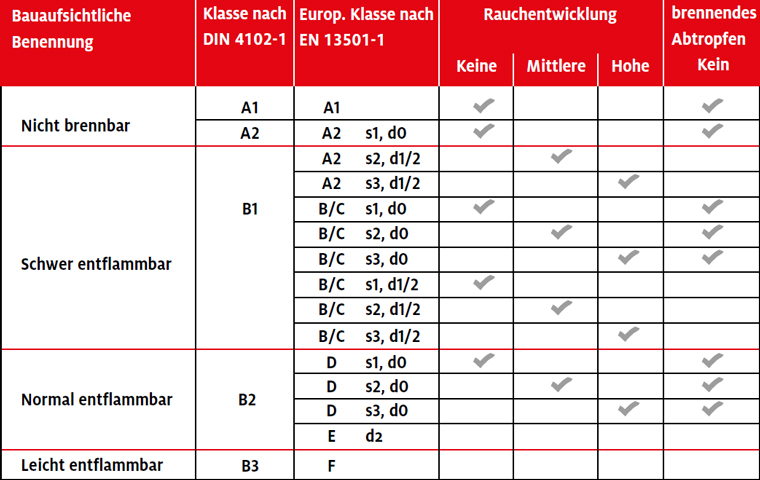
A1, A2, B, C, D, E, F stand for the class; s1, s2, s3 for smoke development (smoke); d0, d1, d2 for burning droplets (drop). As these criteria can be combined in the A2, B, C, D range, it is possible to make more precise statements about the extent to which smoke formation and dripping/dropping cause additional hazards, particularly in the case of combustible building materials.
Other regulations, e.g. Great Britain
Despite European harmonisation, each country is committed to this topic with different interests and different levels of intensity. In England, for example, the Building Regulations 2010, section ‘Fire safety’ under Regulation 7 (as a kind of warning shot) also stipulate that all building materials used in an external façade must fulfil the European classification of A2-s1, d0 or Class A1.
Exceptions include sealing films and membranes, which are regulated in paragraph 12.16 of Approved Document B 2019. This paragraph requires a minimum classification of B-s3, d0 (high smoke development, no burning droplets) for films and membranes above the ground surface. The structurally necessary properties of films and membranes must of course continue to be maintained, so that paradoxical conditions sometimes arise and ultimately planners and façade builders often have to obtain an exclusion.
The main points of criticism are:
- Inadequate diffusion gradient of the solutions offered
- Processability of the materials
- Durability of the materials
- Flexibility and water resistance of the materials
- Durable functionality
This might also interest you

New TEROSON Profi Guide
The TEROSON Profi-Guide is the ultimate, easy-to-read reference work for waterproofing professionals.

TEROSON product range
Download the TEROSON product programme and get detailed information about our products.

Products at a glance
From waterproofing to coating: Discover TEROSON's comprehensive range of products at a glance.
Do you need technical advice?
Our TEROSON team is at your disposal.
Get in touch with us!